Micro-metallographic analysis is a technique widely used in the field of metallurgy, which helps us to deeply understand and know the properties of metallic materials by observing and analyzing their organizational structure and properties. In this paper, we will introduce the significance and methods of micro-metallographic analysis and discuss its importance in materials science research and engineering practice.
The significance of microscopic metallographic analysis
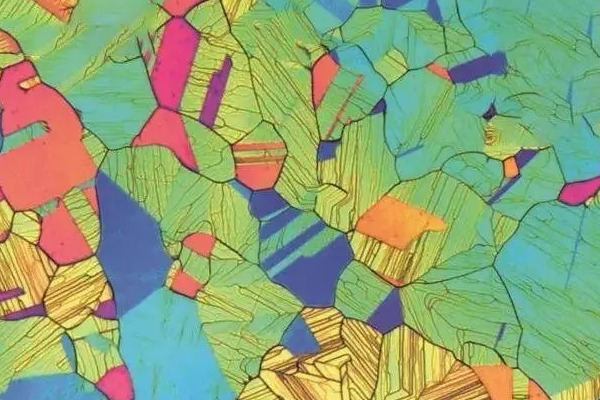
Microscopic metallographic analysis can reveal a variety of information about the grain structure, grain boundaries, twinning, hardness, etc. of metallic materials, which provides us with a basis for in-depth study and understanding of materials. By analyzing the microstructure of metallic materials, we can study the organization evolution law of the materials, explore the reasons for the changes in the properties of metallic materials, and then guide the design, preparation and application of metallic materials.

Methods of microscopic metallographic analysis
Micro-metallographic analysis includes a range of experimental and observational methods, several of which are commonly used are described below:
Metallographic microscope
Metallographic microscopy is a commonly used method for observing the microstructure of metallic materials. It enables us to clearly observe the grains, grain boundaries and other structural features of a metallic material through a magnifying and focusing lens. Through metallographic microscopy, we can obtain information about the grain size, grain morphology, and the type and density of grain boundaries of a material.
Metallographic corrosion
Metallographic etching is a method of observing the microstructure of a material by chemically dissolving it. By immersing a metallic material in a specific corrosion reagent for a period of time, it is possible to make specific tissue structures or phases easier to observe relative to other tissue structures or phases. Metallographic corrosion can be used to observe grain morphology, connectivity of grain boundaries, and non-metallic inclusions.
Microhardness Testing
Microhardness testing is a method to understand the mechanical properties of a material by measuring the microhardness of its surface. Using a micro hardness tester, we can measure the hardness of a material on a microscopic scale, and then study the deformation behavior and deformation resistance of the material, etc. Micro hardness testing can help us evaluate the strength, toughness and wear resistance of metallic materials.
Application of microscopic metallographic analysis
Micro-metallographic analysis has a wide range of applications in materials science research and engineering practice. It can be used in the evaluation and improvement of material properties, quality control of materials and failure analysis. For example, microscopic metallographic analysis can help us study the grain growth behavior of metallic materials, optimize the heat treatment process of materials, and improve the strength and toughness of materials. It can also help us detect defects and inclusions in materials, predict the life of materials, and reduce the risk of material failure. In addition, micro-metallographic analysis can be used to study the wear mechanism of materials, improve the friction properties of materials, and increase the wear resistance of materials. It plays an important guiding role in the selection, design and manufacturing of materials.
Conclusion
Microscopic metallographic analysis is an important material analysis technique, which reveals the organization characteristics and performance change mechanism of materials by observing and analyzing the microstructure of metallic materials. It has a wide range of applications in materials science research and engineering practice, and provides an important basis and guidance for the research and development and application of materials. We believe that, with the continuous development of technology and in-depth research, micro-metallographic analysis will play an even more important role in the field of metallurgy.